In the realm of fire safety, two critical terms often arise: fire integrity and fire insulation. While they may sound similar, they represent distinct concepts with significant implications for building design, construction, and safety measures. Understanding the difference between fire integrity and fire insulation is crucial for architects, engineers, and anyone involved in fire protection. In this article, we will delve into the depths of these concepts, unravel their disparities, and explore their practical applications.
- Defining Fire Integrity:
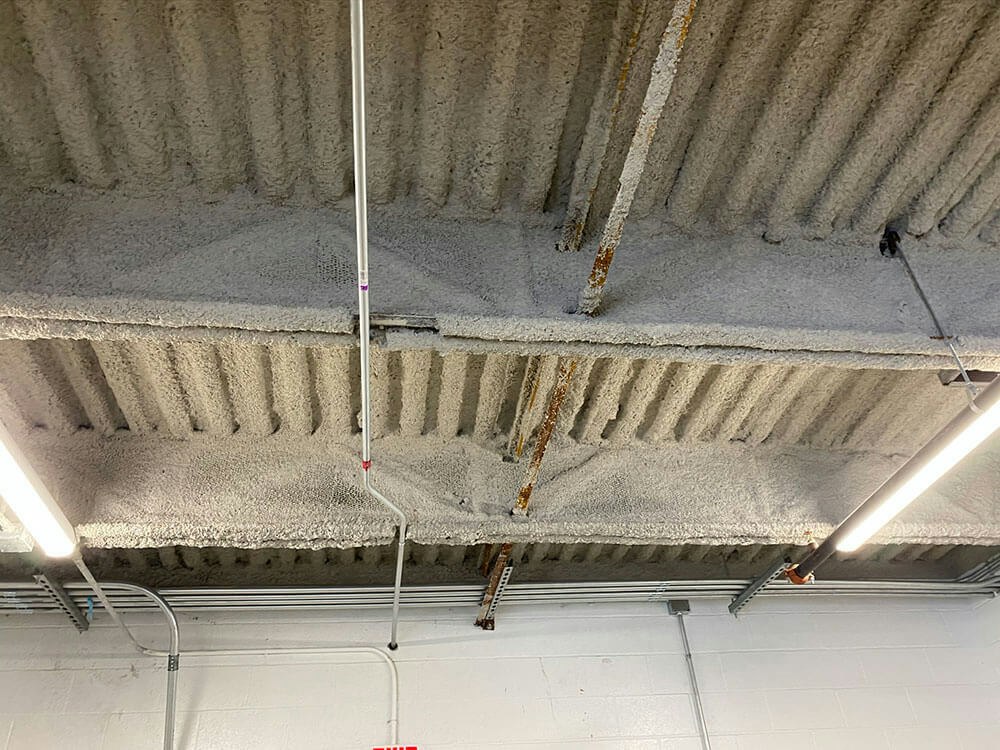
Fire integrity refers to the ability of a structural element or assembly to maintain its load-bearing capacity and structural stability during a fire. It focuses on preventing the collapse or failure of the structure, ensuring the safety of occupants and facilitating the work of firefighters. Fire integrity is typically measured in terms of the duration for which a structure can withstand fire exposure without compromising its structural integrity. - Exploring Fire Insulation:
Fire insulation, on the other hand, pertains to the ability of a material or assembly to resist the transfer of heat during a fire. It involves the use of fire-resistant materials and systems to limit the spread of fire and protect adjacent areas from its damaging effects. Fire insulation aims to contain the fire within a specific area, allowing occupants to evacuate safely and granting firefighters time to control the situation. - Key Differences:
While both fire integrity and fire insulation contribute to overall fire safety, their primary distinctions lie in their objectives and focus areas. Fire integrity emphasizes the structural stability of a building, ensuring it remains intact during a fire. It involves measures such as fire-resistant structural elements, proper compartmentalization, and adequate fireproofing of critical components.
On the other hand, fire insulation concentrates on preventing the spread of fire and limiting its impact on adjacent areas. It involves the use of fire-resistant materials, such as fire-rated walls, doors, and firestops, to create barriers that impede the passage of flames, smoke, and heat. Fire insulation strategies also encompass the installation of fire suppression systems, such as sprinklers, to control the fire's growth and extinguish it.
- Practical Applications:
Understanding the difference between fire integrity and fire insulation is crucial when designing and constructing buildings. Architects and engineers must consider both aspects to ensure comprehensive fire protection. They need to select appropriate fire-rated materials, design effective compartmentalization systems, and incorporate fire suppression measures to achieve optimal fire safety.
Moreover, building codes and regulations often mandate specific fire integrity and fire insulation requirements based on the building's occupancy type, height, and usage. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure the safety of occupants and meet legal obligations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, fire integrity and fire insulation are distinct yet interconnected concepts within the realm of fire safety. Fire integrity focuses on maintaining the structural stability of a building during a fire, while fire insulation aims to limit the spread of fire and protect adjacent areas. Architects, engineers, and fire safety professionals must comprehend these differences to implement appropriate measures and ensure comprehensive fire protection. By prioritizing both fire integrity and fire insulation, we can create safer built environments that withstand the challenges posed by fire incidents.