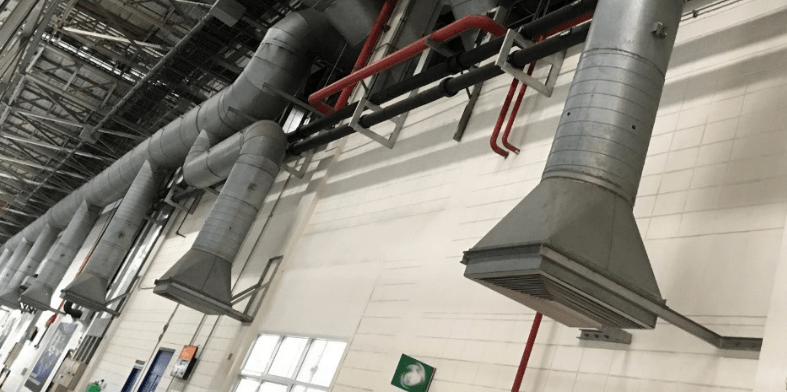
In the realm of architecture, buildings are not just static structures; they possess a dynamic quality that allows them to "breathe." Ventilation, the process of exchanging indoor and outdoor air, plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and comfortable environment within buildings. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate mechanisms of how buildings breathe and explore the various ventilation strategies employed in modern architecture.
- The Importance of Ventilation:
Ventilation serves multiple purposes beyond simply providing fresh air. It helps regulate temperature, control humidity levels, remove pollutants, and prevent the buildup of harmful gases. Proper ventilation enhances indoor air quality, promotes occupant well-being, and contributes to energy efficiency. - Natural Ventilation:
Natural ventilation harnesses the power of natural forces, such as wind and buoyancy, to facilitate air movement. It involves strategically placed openings, such as windows, vents, and skylights, to allow for the intake and exhaust of air. By utilizing prevailing winds, stack effect, and cross ventilation, natural ventilation can effectively cool and ventilate buildings while minimizing energy consumption. - Mechanical Ventilation:
In situations where natural ventilation is insufficient or impractical, mechanical ventilation systems come into play. These systems utilize mechanical devices, such as fans, blowers, and air conditioning units, to circulate and condition the air. Mechanical ventilation offers precise control over air distribution, filtration, and temperature, ensuring optimal indoor conditions regardless of external factors. - Hybrid Ventilation:
Combining the advantages of both natural and mechanical ventilation, hybrid ventilation systems offer a flexible and energy-efficient solution. These systems intelligently integrate natural ventilation strategies with mechanical components to adapt to changing weather conditions and occupant needs. By optimizing the use of natural resources and minimizing reliance on mechanical systems, hybrid ventilation strikes a balance between sustainability and comfort. - Ventilation Design Considerations:
Effective ventilation design requires a comprehensive understanding of building orientation, site characteristics, climate conditions, and occupant requirements. Factors such as building envelope design, air distribution pathways, filtration systems, and noise control measures must be carefully considered to achieve optimal ventilation performance. Advanced technologies, such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, enable architects and engineers to analyze and optimize ventilation designs for maximum efficiency.
Conclusion:
Ventilation is an essential aspect of building design that directly impacts the health, comfort, and productivity of occupants. By embracing innovative ventilation strategies, architects and engineers can create sustainable and livable spaces that harmonize with the environment. Understanding how buildings breathe and implementing effective ventilation systems is not only crucial for the well-being of occupants but also for the overall sustainability of our built environment.