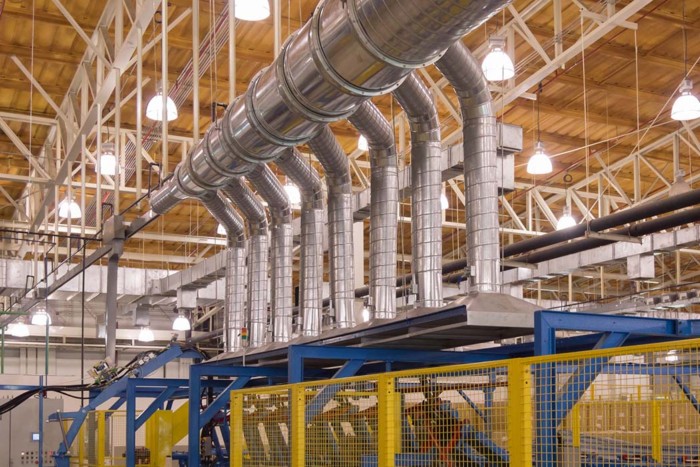
Building ventilation systems play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and ensuring a comfortable and healthy environment for occupants. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate workings of these systems, exploring their components, functions, and the science behind their operation.
- Understanding the Basics:
To comprehend how building ventilation systems work, it is essential to grasp the fundamental principles that govern their functioning. Ventilation systems primarily aim to remove stale air and introduce fresh air into the building, thereby controlling temperature, humidity, and pollutants. - Components of Building Ventilation Systems:
a. Air Intake: The ventilation system begins with an air intake, which draws in fresh outdoor air.
b. Air Filters: As the outdoor air enters the system, it passes through filters that remove dust, allergens, and other particulate matter.
c. Fans: Fans are responsible for moving the air through the system, ensuring proper circulation and distribution.
d. Ductwork: The ductwork acts as a network of pathways, delivering the conditioned air to different areas of the building.
e. Exhaust Systems: These systems remove stale air, odors, and pollutants from the building, maintaining a healthy indoor environment. - Ventilation Strategies:
a. Natural Ventilation: This strategy utilizes natural forces like wind and temperature differences to drive air movement.
b. Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical systems employ fans and other equipment to actively control and distribute air.
c. Hybrid Ventilation: Combining elements of both natural and mechanical ventilation, this strategy optimizes energy efficiency and indoor air quality. - Ventilation Rate and Air Changes per Hour (ACH):
The ventilation rate refers to the amount of outdoor air supplied to a space per unit of time. Air Changes per Hour (ACH) measure the number of times the entire volume of air within a space is replaced in one hour. These metrics are crucial in determining the effectiveness of a ventilation system in maintaining air quality. - Energy Efficiency Considerations:
Building ventilation systems should strike a balance between providing adequate air exchange and minimizing energy consumption. Energy recovery systems, such as heat exchangers, can help reduce the energy requirements of ventilation systems by transferring heat or coolness between the incoming and outgoing air streams.
Conclusion:
Building ventilation systems are intricate networks of components and strategies designed to ensure optimal indoor air quality. By understanding the basics, components, ventilation strategies, and energy efficiency considerations, we can appreciate the importance of these systems in creating healthy and comfortable indoor environments.